A static function is a function whose scope is limited to the current source file. Scope refers to the visibility of a function or variable. If the function or variable is visible outside of the current source file, it is said to have global, or externalscope. If the function or variable is not visible outside of the current source file, it is said to have local, or static scope.
意思是說靜態函式只能被該檔案所看見,其它檔案無法得知該檔案是否有其靜態函式。
有一些 C 的語法,在 C++ 的程序員相對少用。但就是因為這個原因,有時就會忽略了。
假設我們有一個Header檔 Foo.h:
static void f1(){
cout << “f1()" << endl;
}
cout << “f1()" << endl;
}
void f2(){
cout << “f2()" << endl;
}
cout << “f2()" << endl;
}
f1 和 f2 的差別在於 static 這個 keyword 。在這裡的 f1 被宣告和定義為 static ,是指它只在這個 Compilation Unit 中生效。而 f2 沒有被定義為 static ,亦即是它可以被其他 Compilation Unit 訪問。
但到底什麼是 Compilation Unit 呢?首先,一個程式編譯過程如下:
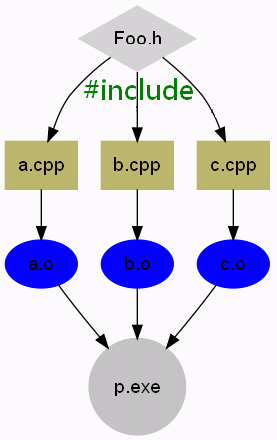 這裡的 a.cpp , b.cpp 和 c.cpp 也 引入了 Foo.h 這個檔案,經過前處理器後,Foo.h 的內容會被加入到 a.cpp, b.cpp 和 c.cpp 中,再經過編譯器,變成為 a.o , b.o 和 c.o 這些目的碼,最後經過連結器,變成執行檔。
這裡的 a.cpp , b.cpp 和 c.cpp 也 引入了 Foo.h 這個檔案,經過前處理器後,Foo.h 的內容會被加入到 a.cpp, b.cpp 和 c.cpp 中,再經過編譯器,變成為 a.o , b.o 和 c.o 這些目的碼,最後經過連結器,變成執行檔。
要留意的地方是,每個經過前處理器處理後的.cpp 檔,和它的目的檔是一一對應的,而Compilation Unit,就是這些被處理後的.cpp 檔了。
若以Foo.h 的 f1 為例子,雖然在每個 .cpp 檔也被定義了,但經過編譯後,所有的f1 也會被隱藏在自己的目的檔中,連結器在找尋symbol的過程中,是會忽略的。
但f2 就不同了,所有的f2 在目的檔中,也是不會被隱藏,所以在連結器找尋symbol,會找到多份的f2,那連結就會有錯誤了。
所以在大部份的情況下,在Header檔中定義函數,也是需要 static 這個 keyword 的。就算加上了 inline,情況也是一樣的。
static inline void f3(){
cout << “f3()" << endl;
}
cout << “f3()" << endl;
}
沒有留言:
張貼留言